🛡️ Introduction to Spring Security: What, Why, and How
Spring Security is a powerful and flexible framework for authentication and authorization in Java applications. However, for many developers, it remains a complex and sometimes confusing tool. In this article, we’ll explore how to configure Spring Security for HTTP applications, explain its internal behavior, and show how to integrate different security mechanisms.
🔍 What Is Spring Security?
Spring Security provides:
- Authentication — determines who you are.
- Authorization — checks what you’re allowed to do.
- Protection against attacks — such as CSRF, XSS, and session fixation.
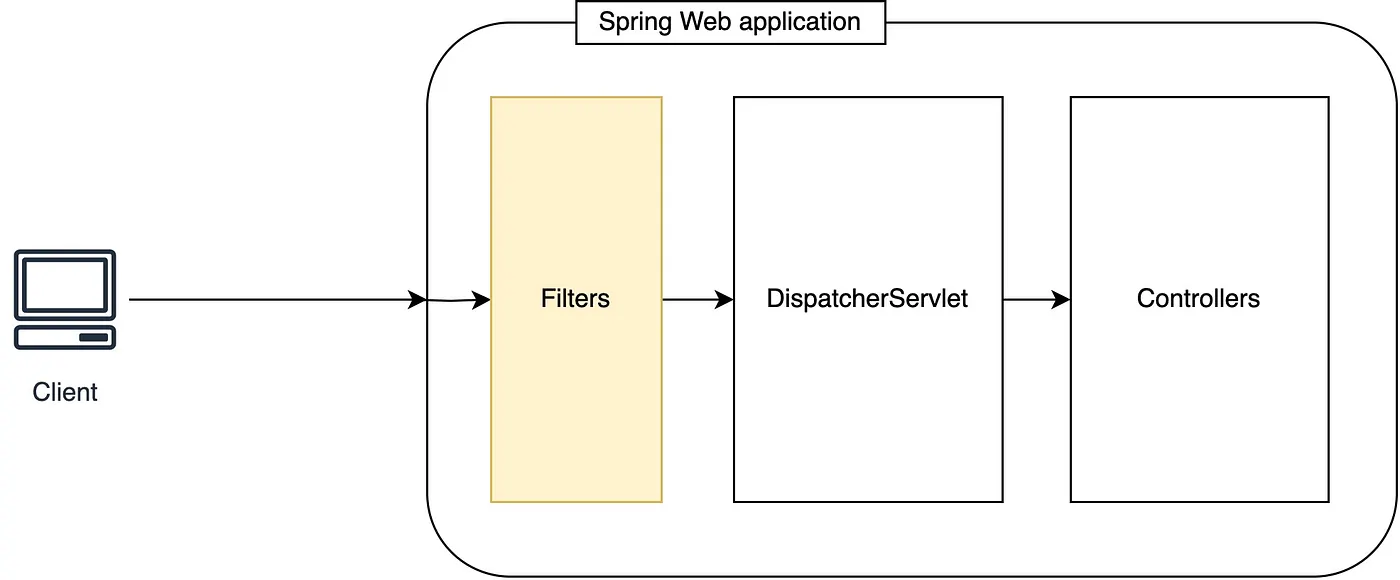
It operates at the filter chain level, securing requests before they reach your business logic.
🧱 Core Components of Spring Security
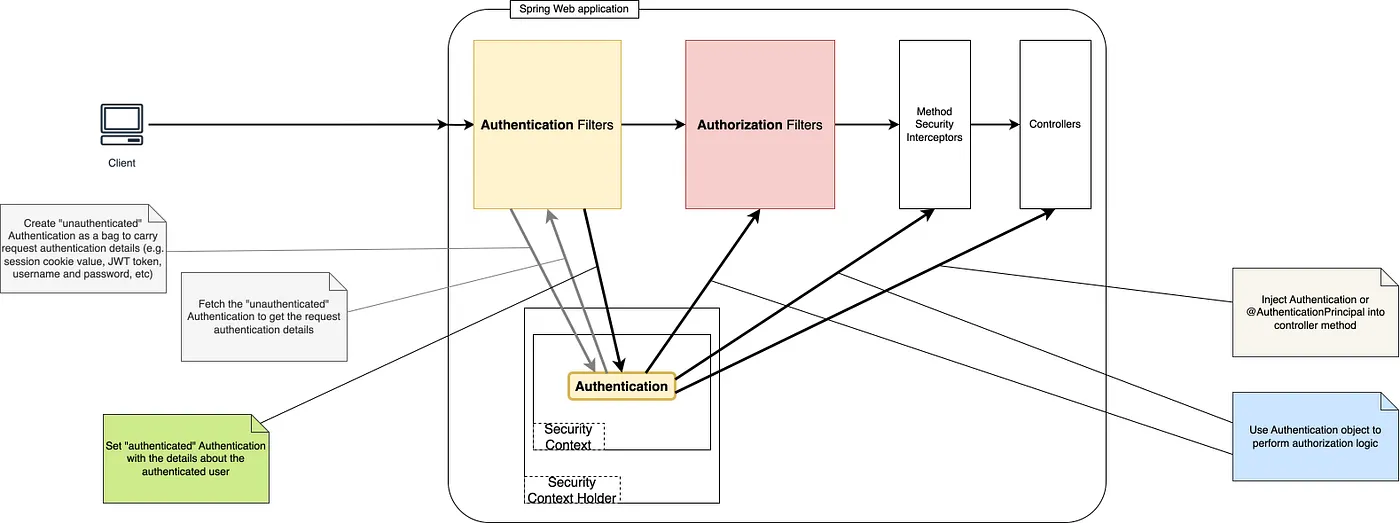
Step-by-step
🧩 Authentication
When an HTTP request arrives, Spring Security checks for valid credentials (e.g., session cookie, JWT token, or Basic Auth header). If none are found or they’re invalid → returns 401 Unauthorized.
🔒 Authorization
Once authenticated, Spring verifies whether the user has permission to access the resource. If not → returns 403 Forbidden.
🛠️ Example Spring Security Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig {
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
return http
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN")
.antMatchers("/user/**").hasAnyRole("USER", "ADMIN")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.and()
.httpBasic()
.and()
.build();
}
}✅ Explanation
/admin/**→ accessible only to users with role ADMIN./user/**→ accessible to both USER and ADMIN roles.- Any other request requires authentication.
- Supports both form login and HTTP Basic authentication.
🧩 Tips for Real Projects
- Use
BCryptPasswordEncoderto securely store passwords. - Disable CSRF only for stateless APIs.
- Consider using JWT for RESTful or microservice-based systems.
- Configure CORS properly if your frontend runs on a separate domain.
🚀 Summary
Spring Security might seem overwhelming at first, but understanding its filter-based architecture and core components makes it much easier to work with. By configuring authentication managers, filter chains, and custom providers correctly, you can secure your Java applications against the most common web vulnerabilities.